Retirement planning can be daunting, yet it is a critical component of financial health. Understanding how much money you need to retire is essential for building a sustainable future post-employment. This blog post will walk you through evaluating your retirement goals, the factors affecting those goals, and tools to help you assess them.
To begin with, we will discuss why setting a retirement goal is necessary, followed by key factors to consider that will influence how much you'll need. We’ll also cover popular retirement calculators and the relevant rules, including the well-known 4% rule, to help guide your planning process.
Finally, we'll look at inflation adjustments, healthcare costs, social security, and pensions, wrapping up with actionable steps to create your retirement roadmap. By the end of this post, you will have a clear understanding of the elements involved in determining your retirement savings needs.
Why a Retirement Goal is Important

Having a retirement goal provides direction and helps create a sense of purpose in your financial planning. By determining how much money you will need to live comfortably in retirement, you are more likely to achieve the quality of life you envision.
Setting a target allows you to break down your savings into manageable steps. It helps you create a monthly budget and encourages consistent saving and investment habits that will contribute to meeting your retirement objective.
Moreover, understanding your retirement goal aids in making informed decisions about lifestyle choices, investments, and spending, ensuring your financial needs are adequately covered when you are no longer working.
Factors to Consider

Several factors can affect how much you need to save for retirement. These include your expected lifestyle during retirement, the age at which you plan to retire, and your estimated life expectancy. Understanding these aspects can help with projecting the funds required over an extended period.
Additionally, it's essential to consider the location where you plan to retire, as housing costs and other living expenses can vary drastically depending on where you live. All these factors together will create a more personalized retirement savings goal.
- Expected monthly expenses during retirement
- Sources of retirement income
- Desired retirement age
- Longevity and health factors
- Inflation rates affecting purchasing power
By understanding the elements that contribute to your retirement goal, you can make better financial decisions that align with your needs.
Common Retirement Calculators
Using retirement calculators can simplify the complex process of planning for retirement. These tools allow you to input your savings, expected retirement age, and projected expenses to estimate how much you will need to save and how long your savings will last.
- 401(k) calculator
- IRA calculator
- Pension calculator
- Social Security calculator
- Retirement savings calculator
These calculators can provide valuable insights and help you assess whether you are on track to meet your retirement goals.
The 4% Rule

The 4% rule is a popular guideline used to determine how much retirees can withdraw from their retirement savings annually without running out of money. It suggests that withdrawing 4% of your initial retirement portfolio each year, adjusted for inflation, should sustain you for about 30 years.
The concept is based on historical market performance and aims to balance your withdrawal rate with growth on your investments. Retirees may adjust this rate based on their individual financial circumstances and market conditions, but the 4% rule serves as a foundational rule of thumb.
It's essential to note that this rule doesn't account for every individual situation, as personal expenses and changes in market conditions can lead to different outcomes. Therefore, while the 4% rule can provide a baseline, evaluating your unique financial picture is crucial.
In summary, consider the 4% rule a starting point for retirement withdrawals, while remaining flexible to adjust your strategies based on new information and changing circumstances.
Personal Savings Rate
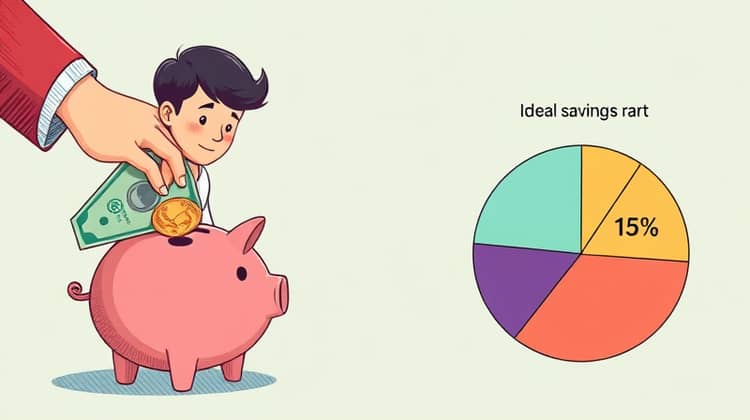

Your personal savings rate directly impacts how much you can accumulate for retirement. It represents the percentage of your income that you save and invest for the future. A higher savings rate typically means a greater pool of funds to draw from during retirement.
Experts recommend aiming for a savings rate of at least 15% of your income for a successful retirement plan. However, those starting later in their careers might need to increase this percentage to catch up.
- Determine your current expenses
- Set a specific retirement savings goal
- Calculate the amount needed for desired retirement lifestyle
- Adjust your monthly budget to meet savings goals
Regularly review your savings progress to stay accountable and make necessary adjustments based on life changes and financial market performance.
Determining Your Retirement Goal

To accurately determine your retirement goal, begin by calculating your total anticipated expenses during retirement. This should include housing, healthcare, leisure activities, and daily living costs. Once you have a rough estimate, you can start planning how to meet that goal.
Next, consider your sources of retirement income, such as pensions, Social Security, and withdrawals from investment accounts. Subtract these income sources from your anticipated expenses to figure out how much you need to draw from your savings.
- Calculate your desired annual retirement income
- Factor in other income sources (like Social Security)
- Identify your expected retirement spending
- Consider any potential income from part-time work
This comprehensive approach to evaluating your retirement goal will help you create a more accurate savings plan and provide peace of mind as you move toward retirement.
Example Calculation

Let's consider a practical example to illustrate how to calculate your retirement needs. Suppose you want an annual income of $50,000 during retirement. According to the 4% rule, to maintain this level of income, you would need a total retirement savings of $1.25 million. This is calculated by dividing your desired annual withdrawal (50,000) by 0.04.
Next, factor in any additional sources of income. If you project receiving $20,000 annually from Social Security, subtract this from your required withdrawal amount. Thus, you would need to withdraw $30,000 from your savings each year.
Using the 4% rule again, to find out how much you need to save, divide $30,000 by 0.04, yielding a retirement savings goal of $750,000.
Finally, be mindful that this calculation should be adjusted with market changes, personal circumstances, and planned lifestyle changes as retirement approaches.
Adjusting for Inflation

Inflation can significantly affect your purchasing power over time, especially in retirement. The cost of living may increase, and the value of your dollar can decrease, making it crucial to plan for these changes. It’s important to factor inflation into your calculations for a sustainable retirement.
One common approach is to assume an average inflation rate of 3% to 4% per year when estimating future expenses. This will help ensure that your retirement savings will still suffice as prices rise for goods and services.
Health Care Costs

Health care expenses tend to be one of the most substantial costs individuals face during retirement. As people age, their medical care needs often increase, leading to a significant financial burden. Therefore, it’s vital to factor these potential expenses into your retirement planning.
Consider the cost of premiums for Medicare or other healthcare coverage and out-of-pocket expenses for medications, doctor visits, and long-term care when determining your retirement savings goal.
Social Security and Pensions

Social Security is a key element in most retirees' financial plans. While it's not a guarantee of a comfortable retirement, it provides a stable stream of income to help cover living expenses. Understanding how Social Security works—alongside any pensions you may have—is essential for estimating your retirement income.
To best plan for a secure retirement, it is recommended that you calculate your anticipated Social Security benefits and evaluate any pensions based on service years and contribution amounts. Keep in mind that these income streams may not cover all your expenses, necessitating additional savings.
It's also important to stay informed about any changes to Social Security policies that may impact your benefits in the future. Adapt your financial strategy accordingly to ensure your retirement plan remains robust and realistic.
Thus, Social Security and pensions can play a significant part in your overall retirement picture, but they should be viewed as part of a broader strategy that includes savings and investments.
Conclusion

Ultimately, determining how much you need to retire involves careful consideration of your personal goals, expected expenses, and various income sources. By establishing a retirement goal and working toward it methodically, you can pave the way for a financially secure future.
Using the tools and strategies outlined in this article, you can craft a comprehensive retirement plan tailored to your unique circumstances. Regularly reviewing and adjusting your plan as life changes will also contribute to its effectiveness.
With diligent planning and a proactive approach, you can enter retirement with confidence, ready to enjoy the fruits of your labor without financial worry.