A personal line of credit can be a valuable financial tool for those looking to manage their expenses or finance unexpected costs. Unlike traditional loans that provide a lump sum, a line of credit offers flexibility and access to funds as needed. This can be especially useful in times of need or for those who want to keep their options open without committing to a fixed loan.
Understanding the various aspects of personal lines of credit, including their benefits and potential downsides, can help you make informed decisions. This blog post will delve into what a personal line of credit is, how it functions, its eligibility requirements, and more. By the end, you will have a clearer picture of whether such a financial product is right for you.
With many financial institutions offering personal lines of credit, knowing the differences in types, terms, and associated costs is essential for your financial wellbeing. Let's dive into the details of what a personal line of credit entails.
What is a Personal Line of Credit?
A personal line of credit is a revolving credit account that allows you to borrow money up to a certain limit as needed. It’s essentially a mix between a credit card and a personal loan, which often gives borrowers more flexibility in how they use the funds. You can draw on your line of credit whenever you need to, repay it, and borrow again up to your credit limit.
Unlike a traditional loan, where you receive a lump sum and pay interest on the entire amount, with a line of credit, you only pay interest on the money you actually borrow. This makes it a cost-effective option for short-term financing or managing liquidity issues.
Personal lines of credit can be secured or unsecured, meaning they can require collateral or not, depending on the lender and the borrower’s creditworthiness. This versatility makes them an attractive option for various financial needs.
How Does a Personal Line of Credit Work?
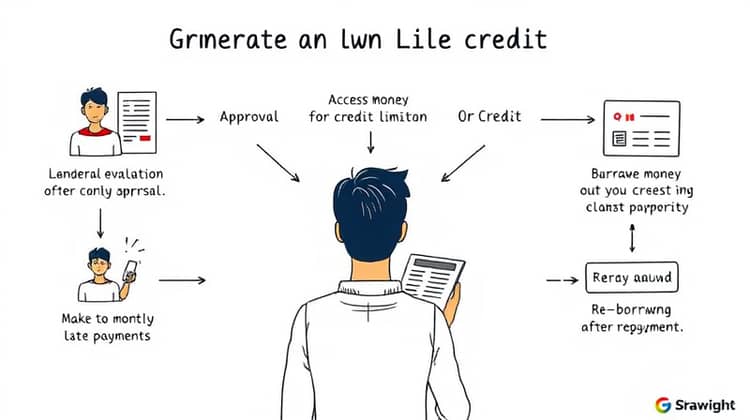
When you apply for a personal line of credit, the lender will evaluate your creditworthiness based on factors such as your credit score, income, and existing debts. If approved, you will be given access to a credit limit, which you can draw from at any time like a credit card.
Once you take money from the line of credit, you will have to make monthly payments, which often include at least interest on the borrowed amount, but can also include a portion of the principal. After you've repaid the borrowed amount, you can borrow from your line again.
Eligibility Requirements
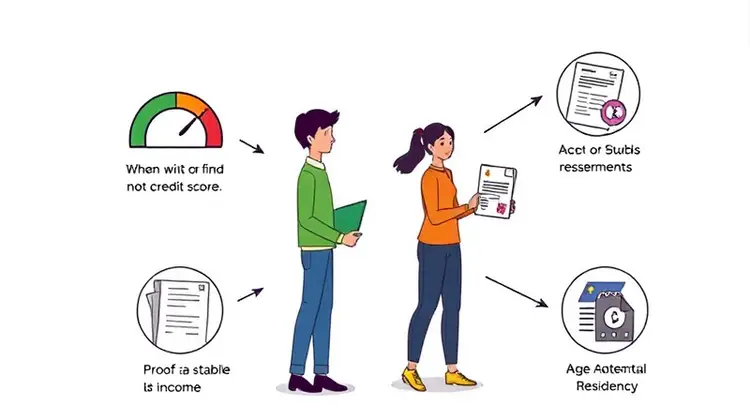
To qualify for a personal line of credit, most lenders have certain eligibility criteria that potential borrowers must meet. Generally, lenders look for a good credit score, which indicates your reliability in repaying borrowed funds. A score of 670 or higher is typically considered good, although requirements may vary by lender.
Additionally, lenders often require a stable income to ensure that you can make timely repayments. This means you may need to provide proof of income through pay stubs or bank statements. Some lenders may also consider your existing debt-to-income ratio to assess how taking on more credit could affect your financial health.
Lastly, age and residency status may also play roles in your eligibility. Most lenders require that you be at least 18 years old and a resident of the country where you are applying for the credit.
- Good credit score (typically 670 or higher)
- Stable income or employment history
- Low debt-to-income ratio
Understanding these eligibility requirements can save you time and improve your chances of approval. It’s good to gather all necessary documents before applying for a line of credit.
Secured vs. Unsecured Personal Lines of Credit
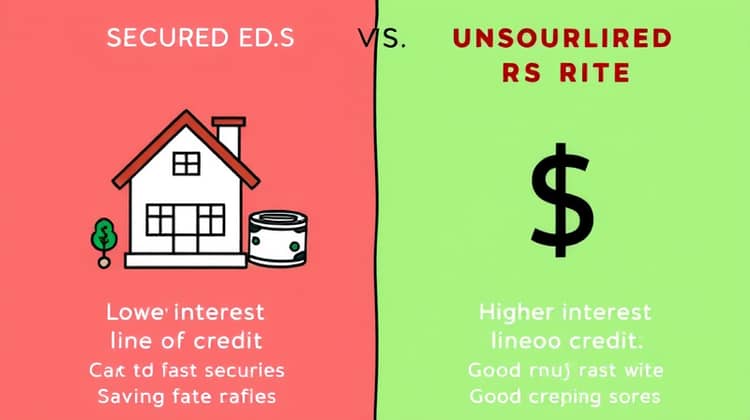
A secured personal line of credit requires collateral, such as your home or savings account. Because you are backing the credit with collateral, secured lines of credit typically have lower interest rates, making them a financially appealing option. However, defaulting on these loans could result in losing your collateral, which is a significant risk.
On the other hand, unsecured personal lines of credit do not require any collateral, but they may come with higher interest rates. Since the lender is taking on more risk without collateral, the cost of borrowing can be higher. Unsecured lines of credit also often require better credit scores for approval.
It’s important to weigh the pros and cons of both types to determine which fits your financial situation best. Consider factors like your credit score, readiness to offer collateral, and how much access to funds you need. Keep in mind your financial behaviors and the risk you are willing to take.
Pros and Cons of a Personal Line of Credit

Like any financial product, personal lines of credit come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages. On the positive side, they offer flexibility, as borrowers can use the funds as needed and only pay interest on the amount drawn. It can serve as a safety net for unexpected expenses, such as medical emergencies or home repairs.
- Flexible borrowing and repayment options
- Only pay interest on the drawn amount
- Can help manage unexpected expenses
Conversely, if not managed properly, it can lead to debt accumulation that may impact your credit score. The ease of access can sometimes encourage overspending, so it’s essential to maintain disciplined financial practices.
How to Apply for a Personal Line of Credit

The first step in applying for a personal line of credit is to research various lenders, including banks, credit unions, and online financial institutions. Compare their terms, interest rates, and eligibility requirements to find the best fit for your circumstances. Make sure to check for any hidden fees that might apply, such as annual fees or withdrawal fees.
Once you’ve identified potential lenders, you’ll need to gather the necessary documentation, which typically includes proof of income, identification, and details of your current debts. Having this information ready will streamline the application process.
Finally, submit your application either online or in person, based on the lender's requirements. Be prepared to wait for approval, as lenders may take a few days to review your application and assess your creditworthiness.
- Research various lenders and their terms
- Gather necessary documentation
- Submit your application
After you submit your application, keep track of its status and be ready to provide additional documentation if requested by the lender.
Key Considerations

Before jumping into a personal line of credit, consider your financial habits and goals. It’s crucial to ensure that you will use the funds responsibly and have a clear repayment plan to avoid falling into a cycle of debt. Understanding how much you may need and when to access the credit is essential.
Additionally, compare several offers to find the one best suited to your financial situation. Interest rates, fees, and terms can vary significantly between lenders, and making an informed choice can save you money in the long run.
Finally, be aware of the impact that taking on more debt can have on your credit score. While a personal line of credit can be a great tool when used wisely, it can also lead to higher debt levels if mismanaged.
Conclusion

In summary, a personal line of credit can be an effective financial product for many individuals. It provides greater flexibility compared to traditional loans and can help manage cash flow during emergencies or expensive life events.
However, it's imperative to understand both the advantages and risks associated with them. By carefully considering your eligibility, understanding the terms, and managing your borrowing and payments responsibly, a personal line of credit can be a valuable asset.














